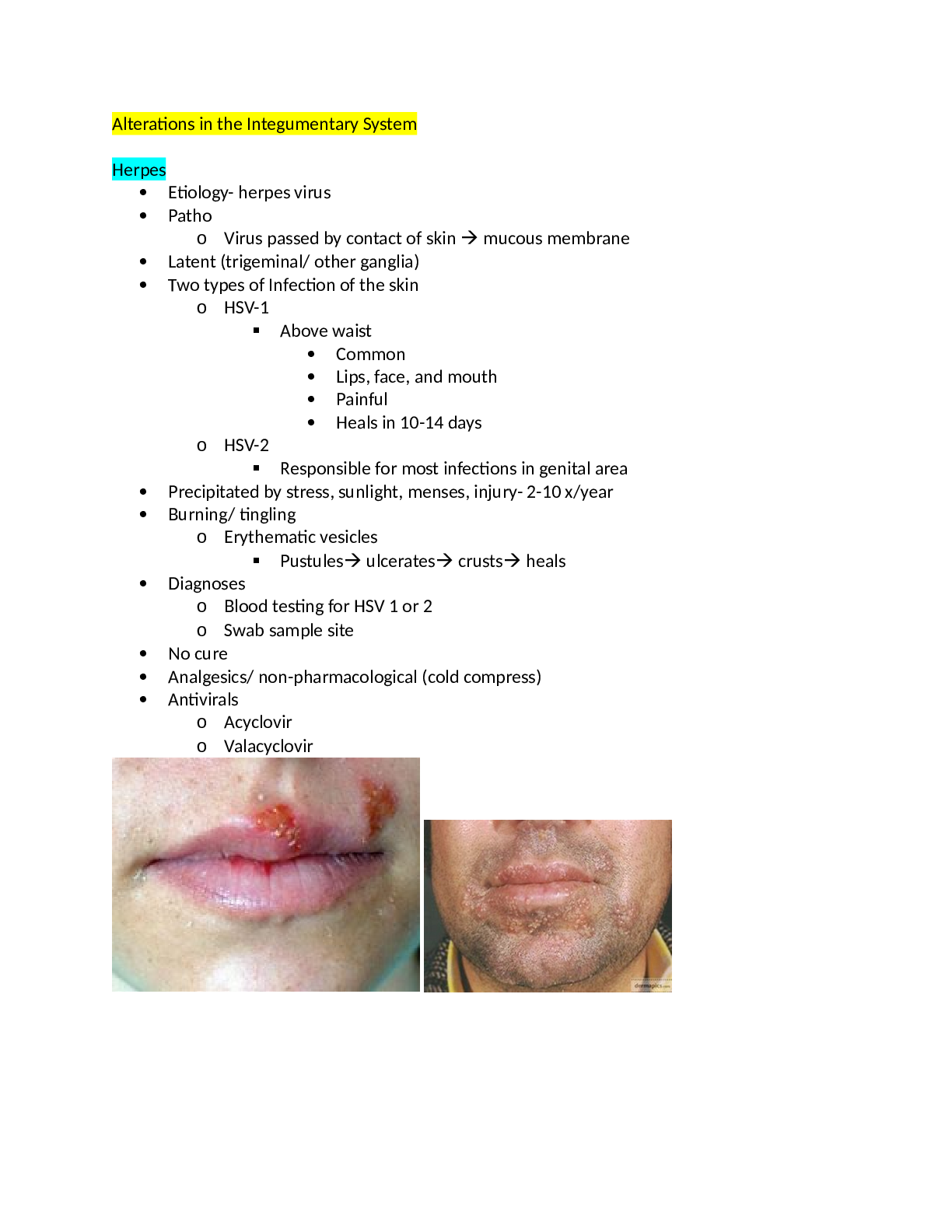
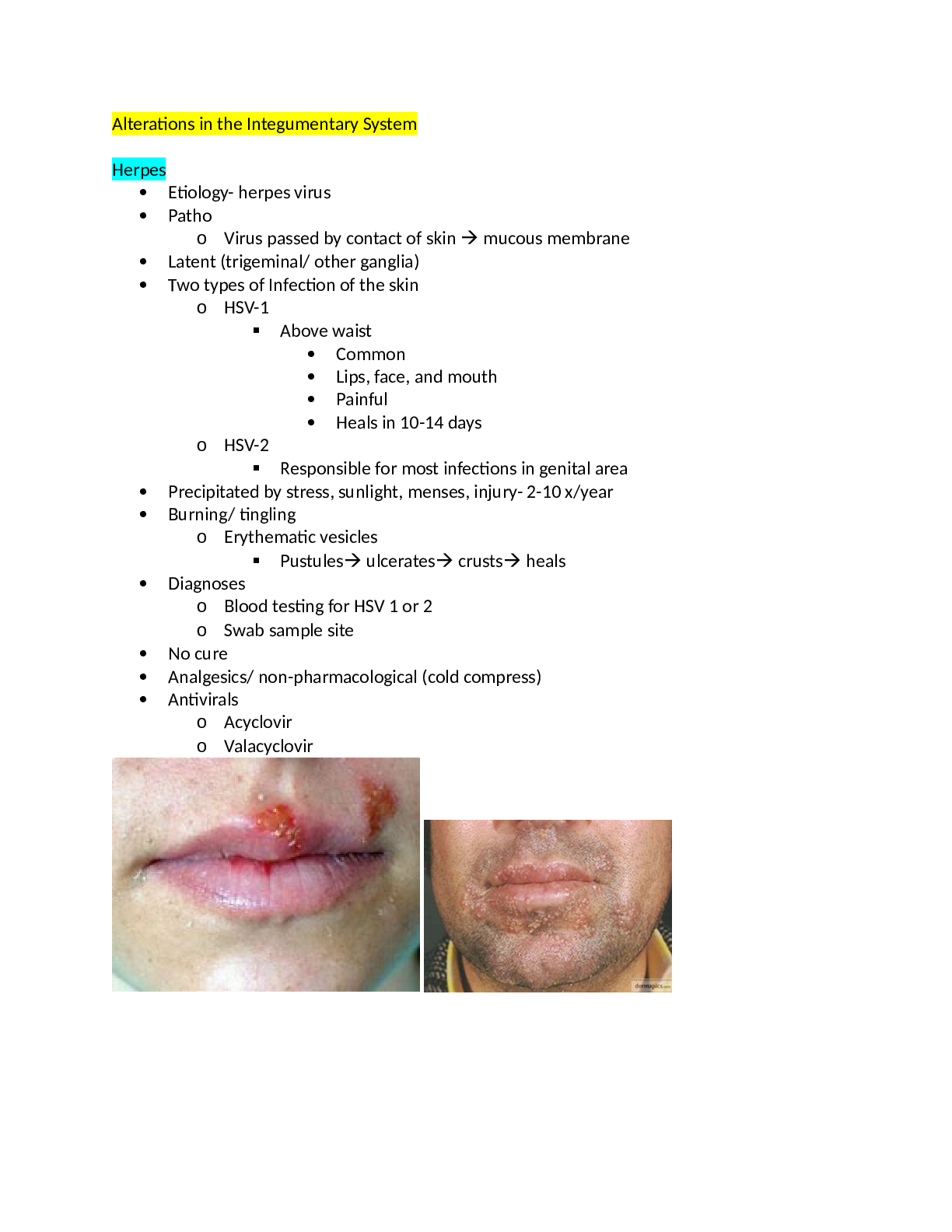
Alterations in the Integumentary System
Course
Subject
Chemistry
Category
Study Guide
Pages
45
Uploaded By
ATIPROS
Preview 5 out of 45 Pages
Download all 45 pages for $ 10.00
Reviews (0)
$10.00
